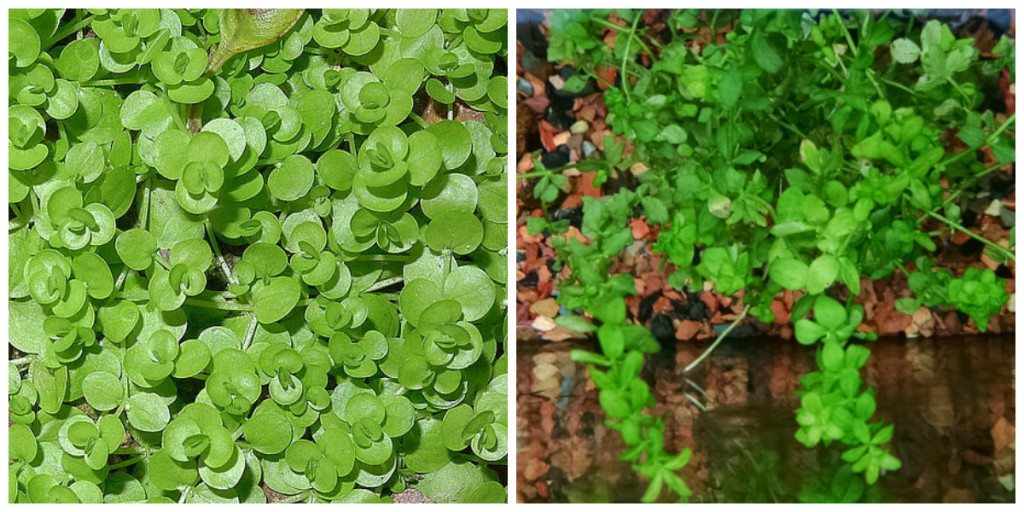
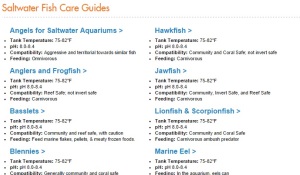
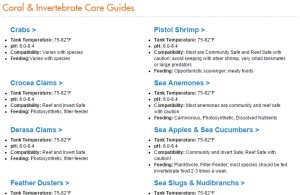
“Baby Tears” is one of the most popular aquarium plants available and is popular as a foreground and midground plant. It has very small leaves and will stay short to cover the bottom under high lighting or will grow taller and bushier under moderate lighting. However, as is often the problem with common names, when we discuss “Baby Tears”, we may be talking about different plants. There are several plants that may be referred to as “Baby Tears”. That description above can apply to any of them. They all have small roundish leaves and grow in similar conditions…so which is the “real” one? That’s as tough to answer as the sneakers/tennis shoes/running shoes/trainers name debate.
“Baby Tears” vs. “Pearl Grass”
The two most common “Baby Tears” available to aquarists are Hemianthus micranthemoides (also called “Dwarf Baby Tears” or Pearl Grass) and Micranthemum umbrosum (the species most often known as Baby Tears, also called “Giant Baby Tears”). The main difference between these two plants is in the leaf shape. M. umbrosum (“Baby Tears”, from here on out) generally has round, almost completely circular leaves. H. micranthemoides (“Pearl Grass”, for the rest of this blog) has elongated leaves, more tear-dropped or elliptical in shape.
Both of these plants have almost identical care and can usually be used interchangeably but there are some small differences here too. Baby Tears is usually easier to care for and tends to grow a bit faster than Pearl Grass, but Pearl Grass is a better foreground plant that will stay shorter and have smaller leaves under high light. Baby Tears tends to be taller and bushier but either can be pruned and trimmed to maintain a height or growth pattern. Both plants can be grown in bunches or on a surface like driftwood, rock or a plastic mat to form a thicker carpet; use fishing line or string to hold it in place under the roots start to attach.
Glossostigma: A Third Look-alike
Another plant, Glossostigma elatinoides (usually shortened to “Glosso”) is also very close to Baby Tears and Pearl Grass in appearance and is sometimes confused with these two plants. It has pairs of small, round leaves that are somewhat in between Baby Tears and Pearl Grass in shape, a rounded teardrop but with the widest and roundest part of the leaf at the end rather than by the stem. They stay short and small under very high light but the leaves will become bigger and taller under lower light. This plant can also be planted in the same way by attaching it to a hard surface or planting each stalk individually until it begins to spread on its own.
Oct 2016 UPDATE: Recent publications have listed that the Pearl Grass found in the aquarium trade may correctly be Hemianthus glomeratus, not H. micranthemoides. Though these two plants are very similar, they have some slight differences in native range and in the flowers. H. micranthemoides may actually be essentially extinct and it is thought that the Pearl Grass known to aquarists in the recent hobby is likely H. glomeratus.
(Baby Tears image by Alex Popovkin, Bahia, Brazil from Brazil (Micranthemum umbrosum (J.F. Gmel.) S.F. Blake) [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons)
 That Fish Blog – Aquarium Advice and Information
That Fish Blog – Aquarium Advice and Information