 Sending flowers is a time-honored way of showing affection and concern, but did you know that your parrots and other feathered pets might appreciate a bouquet as well? I’m not suggesting actually having flowers delivered to your parrot (although I know several who have done that!), but rather that you consider edible flowers as a source of bird food and behavioral enrichment.
Sending flowers is a time-honored way of showing affection and concern, but did you know that your parrots and other feathered pets might appreciate a bouquet as well? I’m not suggesting actually having flowers delivered to your parrot (although I know several who have done that!), but rather that you consider edible flowers as a source of bird food and behavioral enrichment.
The Role of Flowers in Bird Diets
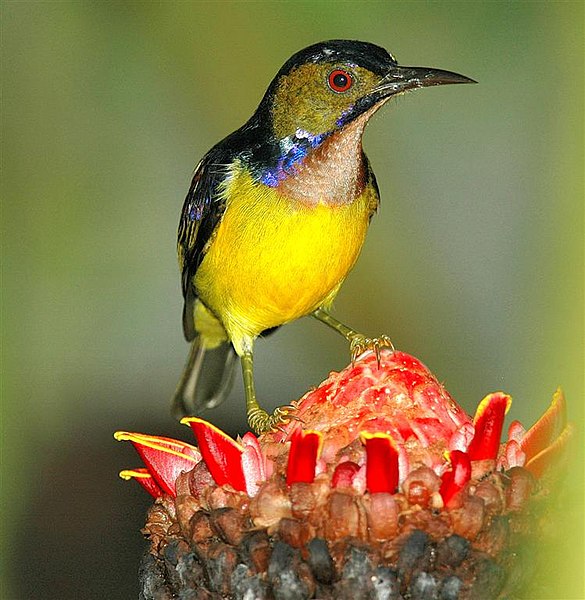
Flowers, buds and nectar figure heavily in the natural diets of many parrots, finches and softbills. In fact, lories and lorikeets are actually “floral specialists” (please see drawing of lorikeet tongue, adapted for nectar feeding). However, with the exception of nectar-mixes, flowers have largely been ignored by most pet keepers.
Flowers are also a major food item of several less commonly-kept softbills, including hummingbirds, sunbirds and the aptly-named flower-peckers. Ornithologists speculate that the brilliant colors of some species may have evolved to provide camouflage during feeding sessions in flowering trees.
Behavioral Stimulation
In addition to their nutritional value, flowers can provide important behavioral stimulation for parrots and other birds. Most parrots delight in tearing them to bits, and bud-covered fruit tree branches (apple, pear, plum etc.) will provide hours of entertainment for both pet and pet-owner. Finches, White-Eyes, Pekin Robins and other small birds will also poke about in flowers for insect treats, real or “imagined”, and may consume petals and nectar as well.
Purchasing Flowers
 Fortunately, it’s quite simple to incorporate flowers into your birds’ diets. Many bird-safe flowers are relished by people, and are available in food stores. In NYC markets, I’ve come across squash, zucchini, rose and daylily flowers (note: not all daylilies are safe for people or birds, so do not pick your own), as well as a number that I did not recognize. Korean, Chinese and Indian neighborhoods have proven especially rich flower-hunting grounds.
Fortunately, it’s quite simple to incorporate flowers into your birds’ diets. Many bird-safe flowers are relished by people, and are available in food stores. In NYC markets, I’ve come across squash, zucchini, rose and daylily flowers (note: not all daylilies are safe for people or birds, so do not pick your own), as well as a number that I did not recognize. Korean, Chinese and Indian neighborhoods have proven especially rich flower-hunting grounds.
Do not buy edible flowers from garden supply outlets or florists, as these will not have been slated for human consumption and would likely have been exposed to toxic chemicals.
Dried flowers specifically marketed as bird food are also a useful option. Goldenfeast’s Hibiscus and Chamomile
may be offered to a variety of parrots, finches and softbills.
Growing and Collecting Flowers for Your Birds
If the option is available to you, growing your own edible flowers is a great alternative to shopping.
Harvesting wild flowers is also possible, but you must be confident in your ability to identify the various species and have access to a pesticide-free collecting site. A field guide will be useful in this regard.
Common, Easy-to-Grow Edible Flowers
The following common flowers are readily accepted by many birds and can easily be grown or, in some cases, purchased at food markets. Do not buy flowers intended as food anywhere other than at a food market; please see above.
Daisy Marigold
 Dandelion Rose
Dandelion Rose
Carnation Sunflower
Violet Zucchini Blossoms
Tulip Squash Blossoms
Elderberry Hibiscus
Impatiens Apple,Plum and Pear Blossoms
Further Reading
Further information on edible and poisonous flowers; written with people in mind but applicable to birds.
Gardening for Pet Birds
Eat Your Roses: a guide to 50+ edible flowers
Lorikeets image referenced from wikipedia and originally posted by Tatiana Gerus
Plain-Throated Sunbird image referenced from wikipedia and originally posted by Ltshears
 Although we are fortunate to have available a wide variety of commercial finch and canary diets, choosing one can be a difficult task. Once a decision is made as to the basic type – seed or pellet – we must then consider the ingredients, which vary from brand to brand. Today I’ll examine some well-known foods and a few often-neglected dietary supplements.
Although we are fortunate to have available a wide variety of commercial finch and canary diets, choosing one can be a difficult task. Once a decision is made as to the basic type – seed or pellet – we must then consider the ingredients, which vary from brand to brand. Today I’ll examine some well-known foods and a few often-neglected dietary supplements. That Bird Blog – Bird Care and History for Pet Birds
That Bird Blog – Bird Care and History for Pet Birds







 Upon fledging, the chicks should be fed on a 6AM – 8PM schedule until they begin pecking at food on their own. Most begin trying solid food on the fifth day after fledging, but this varies widely…close observation is very important at this point.
Upon fledging, the chicks should be fed on a 6AM – 8PM schedule until they begin pecking at food on their own. Most begin trying solid food on the fifth day after fledging, but this varies widely…close observation is very important at this point.