Hey folks Jose here, this time I’m talking about my 10 favorite Tanganyikan Cichlids. These guys didn’t attract me until I saw my first adult Frontosa at a fish show, next thing I know I was breeding shell-dwellers. The main reason I like Tanganyikans is because of their spawning behaviors, but there are some that would rival species from Malawi in beauty, so let’s begin shall we?
Cyprichromis sp. – It’s tough to just pick one variant or species of this genus as a favorite, as there are so many different color variants that occur, but if you want a schooler this is it. Just don’t keep them with aggressive species and Frontosas. They are docile and pretty enough to pack plenty of impact in a group.
Cyathopharynx sp. – Here’s another genus with many color variants. Again, I have a hard time picking just one, although I really love C. foai which I’ve kept and bred. Maybe that makes me partial, but they are absolutely gorgeous fish. In classic featherfin manner, their spawning habits are really interesting to watch. The male shakes and coaxes the female to his crater-shaped nest in the substrate. There the ritualistic and well-choreographed spawning dance continues as the female lays her eggs. The male then entices the female to take her clutch into her mouth by dragging his elongated fins over the sand. As she picks up the eggs he fertilizes them.
Benthochromis tricoti – This 10″ deep water beauty has to be my all time favorite cichlid. The male is striking, especially when he is courting females. Females have a huge mouths despite their small clutch size. One important thing to know about keeping these guys is to keep the lighting on the dimmer side, as it will wash their color out if it is too bright.
Cyphotilapia frontosa – The frontosa is another big fish with a big head…enough said, see one and you’ll know.
 Shell-dwellers (any species) – These are little fish with big fish attitude! There are many different species, but my personal favorite is the Golden Ocellatus. They are fun fish for small tanks where you can really watch them do what they do.
Shell-dwellers (any species) – These are little fish with big fish attitude! There are many different species, but my personal favorite is the Golden Ocellatus. They are fun fish for small tanks where you can really watch them do what they do.
Bathybates sp. – These deep water predators are mainly silver with lots of teeth (like barracuda!). There are 7 species ranging from 9 to 17 inches. They’re not very common in the hobby, but definitely worth keeping if you should see them available and you have a large spare tank aching for something fun to display.
Astatotilapia burtoni – These were my first experience with mouth brooders. I was captivated by the bright egg spots on the male’s anal fin. The very bright orange spots show beautifully against the males varying blue to yellow coloration, which largely depends on his mood. They’re moderately aggressive, but easy to breed and nice to look at.
Enantiopus sp. – This group of cichlids are also known as Flashers, as in the males flash their vivid colors at females during spawning, they are sensitive and delicate and should not be kept with more boisterous species.
Lepidiolamprologus kendalli (nkambae) – This 7 inch predator is  Tanganyika’s version of our Northern Pike. Their aggressive attitude is ample, so make sure you have a tight fitting lid as an individual may try to exclude all other fish from its territory. They’re fish that command respect.
Tanganyika’s version of our Northern Pike. Their aggressive attitude is ample, so make sure you have a tight fitting lid as an individual may try to exclude all other fish from its territory. They’re fish that command respect.
Neolamprologus buescheri – This 3 inch species is a reclusive fish that becomes very aggressive during spawning and towards similar species. A sharp looking fish, they prefer dimly lit tanks with plenty of rock to establish territory.
So that’s my top 10 Tanganyikan Cichlid picks! Next time I will share my picks of favorite Central American Cichlids (yay!)
Please comment and tell me your favorite Tanganyikans, I love to hear the experiences of other cichlid fanatics!
Until next time,
Jose
 That Fish Blog – Aquarium Advice and Information
That Fish Blog – Aquarium Advice and Information

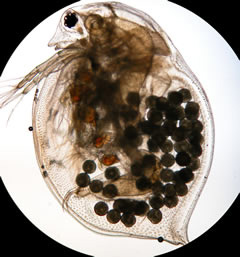 Hello, Frank Indiviglio here. There was a time when all serious aquarists maintained live cultures of Daphnia. This practice has fallen out of favor today, with live foods being replaced by prepared diets. However, many tiny aquatic Crustaceans are easy (and interesting!) to maintain, and represent one of the most nutritious of all food sources for aquatic animals.
Hello, Frank Indiviglio here. There was a time when all serious aquarists maintained live cultures of Daphnia. This practice has fallen out of favor today, with live foods being replaced by prepared diets. However, many tiny aquatic Crustaceans are easy (and interesting!) to maintain, and represent one of the most nutritious of all food sources for aquatic animals.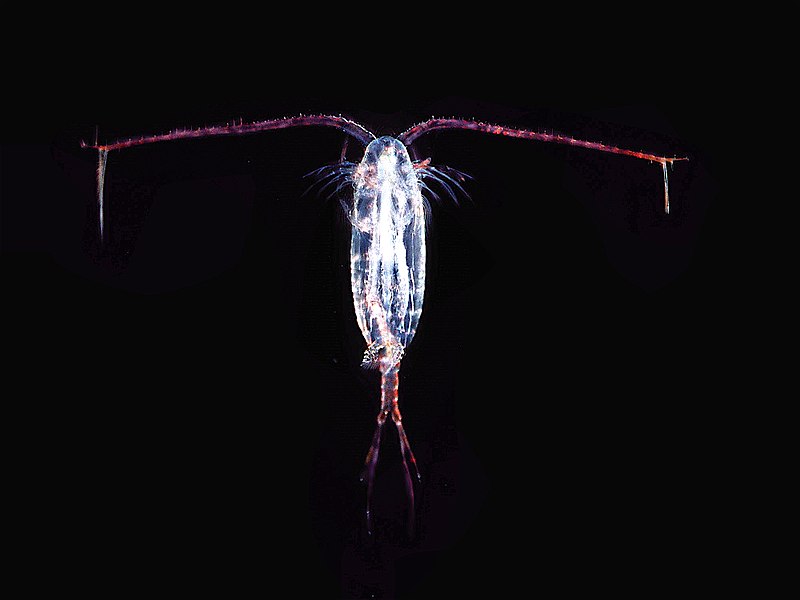
 All American and European eels, whether inhabiting a bay in New Jersey or a pond in England, originated as eggs laid in the Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda. Eels, salmon and many other fishes engage in massive breeding migrations, with millions of adults laying eggs simultaneously and then dying shortly thereafter.
All American and European eels, whether inhabiting a bay in New Jersey or a pond in England, originated as eggs laid in the Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda. Eels, salmon and many other fishes engage in massive breeding migrations, with millions of adults laying eggs simultaneously and then dying shortly thereafter.  The story begins with a single coral larvae finding a small snail shell on which to attach and begin it’s life. From this point the coral can begin to lay down its structure, quickly overgrowing the shell. For one reason or another a Sipunculid Worm moves into the shell, only to become engulfed and trapped inside the coral. This symbiotic relationship allows for constant movement for the coral and safety for the worm. The coral will have a small hole on the bottom allowing for movement and the uptake of sediment by the worm, preferably a fine sand. The worm is a deposit feeder, taking up sand and consuming nutritious organics found in or on the sand. The coral itself is photosynthetic, but with the presence of tentacles during the day, I would suspect they are also planktonic feeders.
The story begins with a single coral larvae finding a small snail shell on which to attach and begin it’s life. From this point the coral can begin to lay down its structure, quickly overgrowing the shell. For one reason or another a Sipunculid Worm moves into the shell, only to become engulfed and trapped inside the coral. This symbiotic relationship allows for constant movement for the coral and safety for the worm. The coral will have a small hole on the bottom allowing for movement and the uptake of sediment by the worm, preferably a fine sand. The worm is a deposit feeder, taking up sand and consuming nutritious organics found in or on the sand. The coral itself is photosynthetic, but with the presence of tentacles during the day, I would suspect they are also planktonic feeders.